Impressive Define Double Replacement Reaction
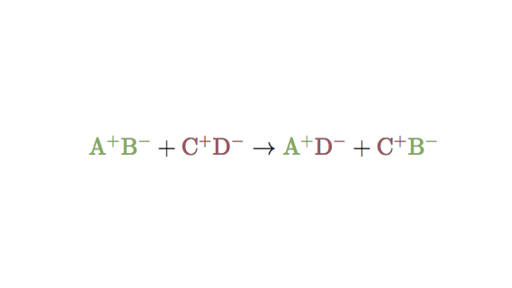
BaCl2 2 NaClO3 Ba ClO32 2 NaCl On concentrating and chilling the resulting mixture barium chlorate precipitates.
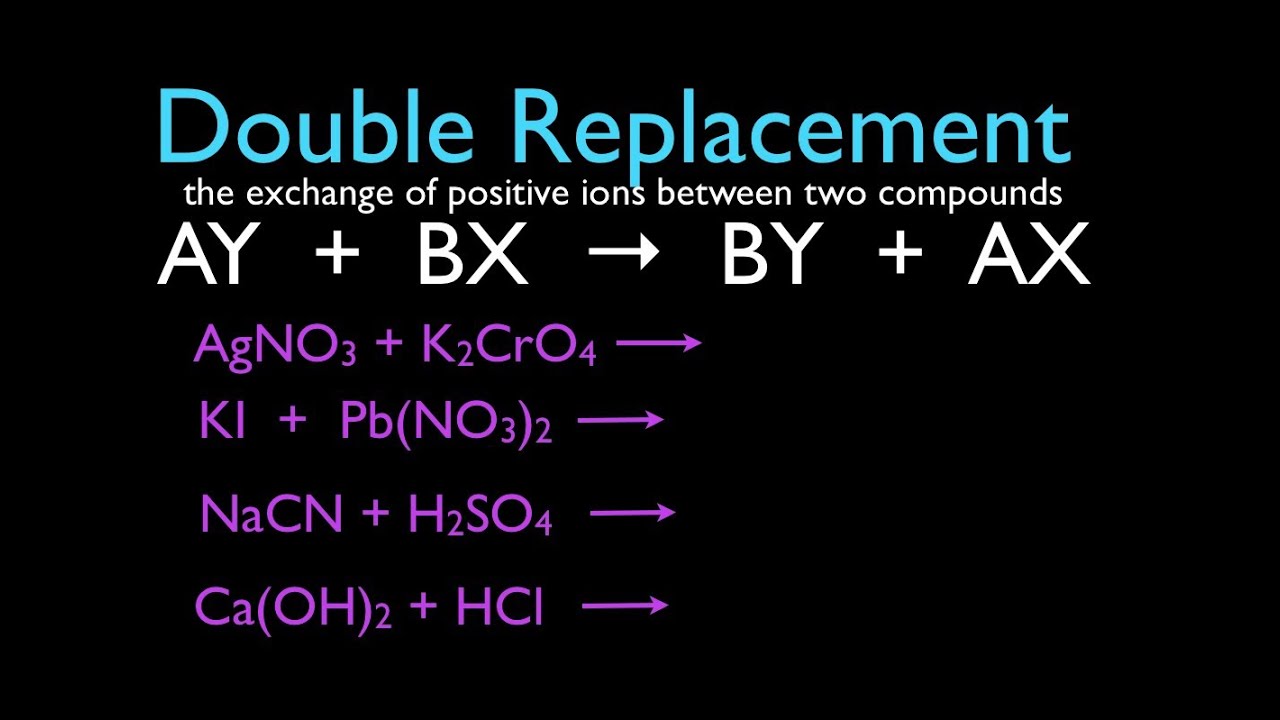
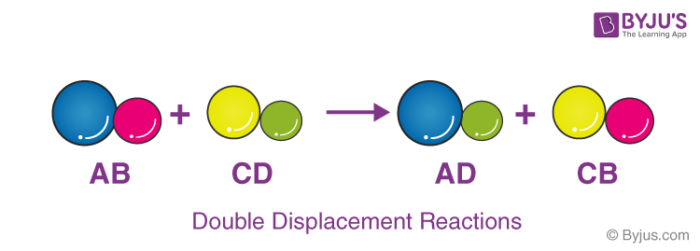
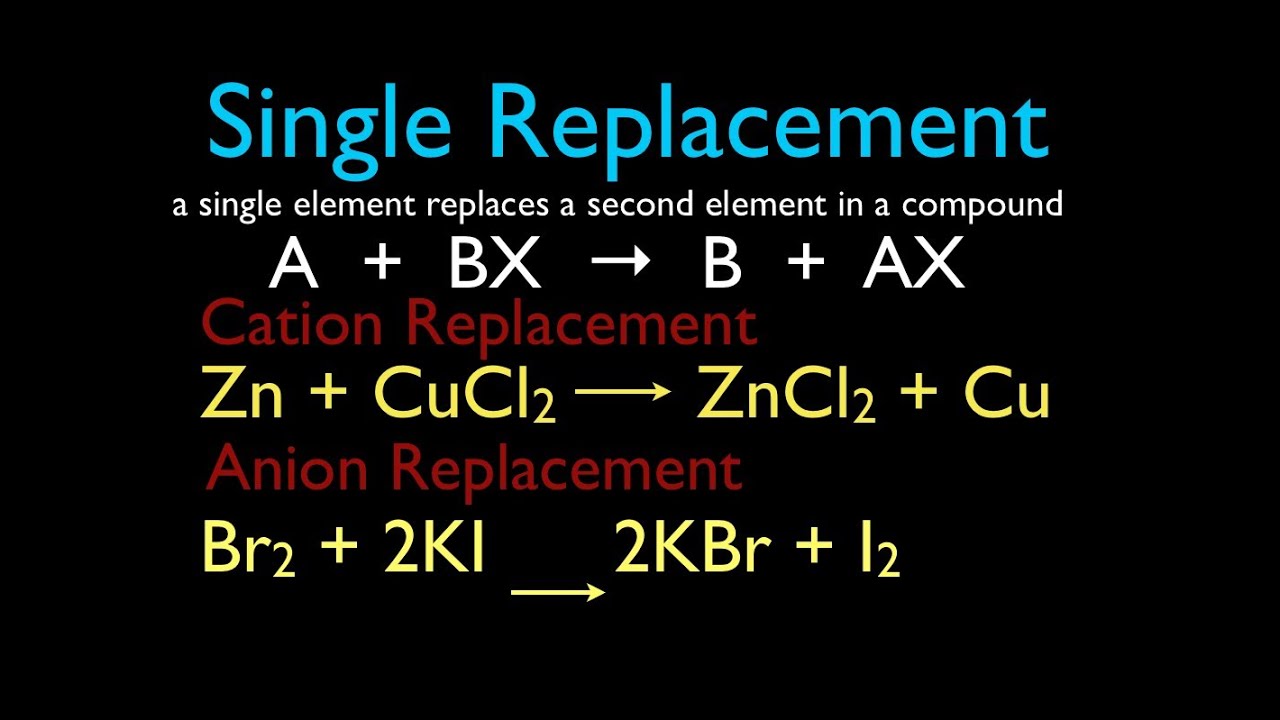
Define double replacement reaction. A double replacement reaction occurs when two ionic compounds exchange ions. Generally it can be represented as follows AB CD. Barium chlorate can be produced through a double replacement reaction between solutions of barium chloride and sodium chlorate.
The general form of a double-replacement also called double-displacement reaction is. Also known as double replacement Usually occurs between two ionic compounds which then in turn create two more ionic compounds. This ScienceStruck post explains the concept of double displacement reaction in chemistry along with a few examples.
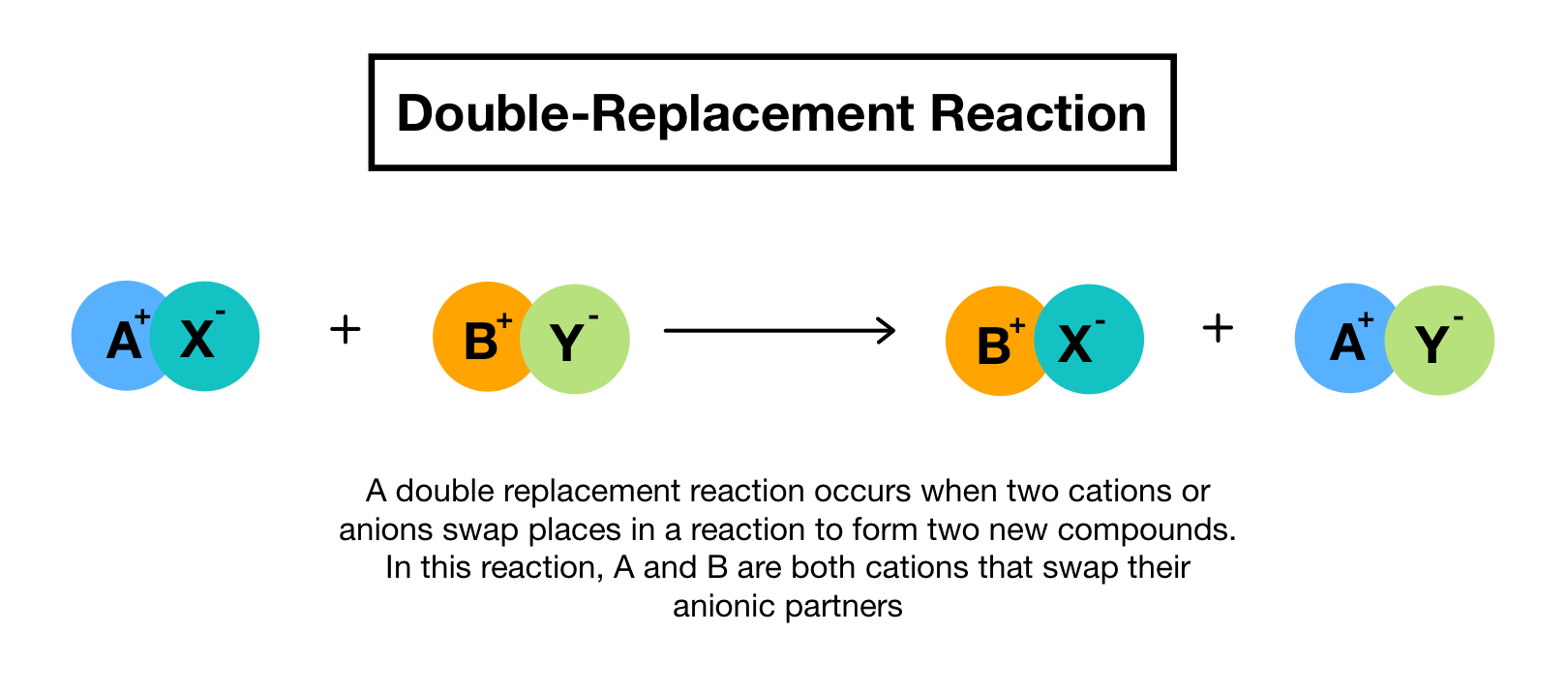
Double replacement reaction - a chemical reaction between two compounds where the positive ion of one compound is. This produces two new ionic compounds. A chemical reaction between two compounds where the positive ion of one compound is exchanged with the positive ion of another compound.
In this reaction and are positively-charged cations while and are negatively. Double replacement reactions are also called double replacement reactions double displacement reactions or metathesis reactions. 1 n a chemical reaction between two compounds where the positive ion of one compound is exchanged with the positive ion of another compound Type of.
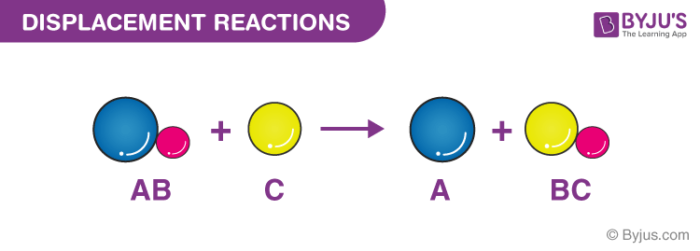
A double replacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction that occurs when two reactants exchange cations or anions to yield two new products. Double decomposition double decomposition reaction metathesis a chemical reaction between two compounds in which parts of each are interchanged to form two new. A double replacement reaction is represented by the general equation.
A double replacement reaction can be represented by the general equation. Two examples are also sho. A chemical reaction between two compounds in which the first and second parts of one reactant are united respectively with the second and first parts of the other reactant.