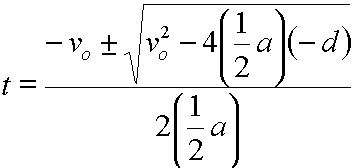Casual Kinematic Equations Rearranged

Because velocity is the antiderivative of acceleration that means that v t a t and v t int a t.
Kinematic equations rearranged. This can be used to determine the final velocity. Rearranging gives the equation in an alternative form. First we need to establish that acceleration is represented by the equation a t -98.
Here we will take a look at the equation that allows us to solve for displacement when the object is constantly accelerating. To keep our focus on high school physics we will not be covering integrals. If rearranged it forms the quadratic equation.
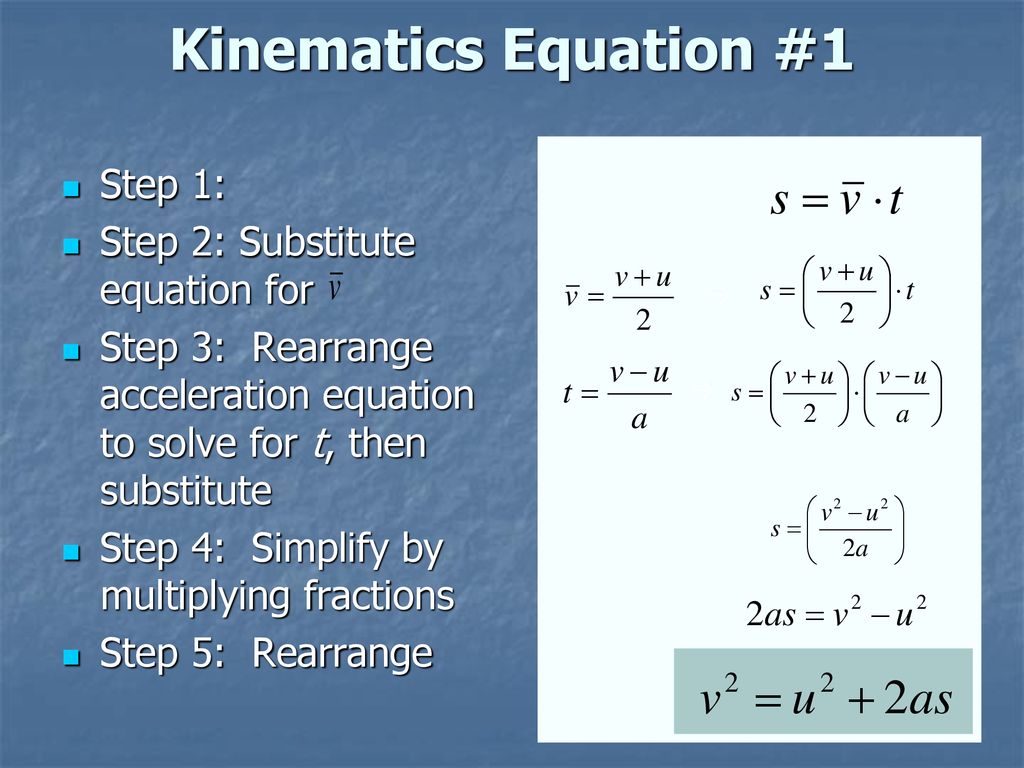
And then expanded to yield. Vf vi a t Final velocity is equal to the sum of initial velocity and acceleration multiplied by time taken. 1 List what quantities are given - will be 3 2 List what is being asked for - will be 13 Find the equation in the table that contains all 4 involved quantities.
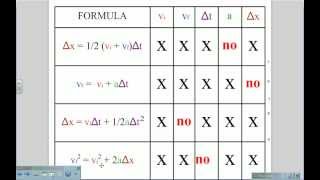
Kinematics equations require knowledge of derivatives rate of change and integrals. Rearranging equations in science the rearrange kinetic energy equation to. The kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be utilized to predict unknown information about an objects motion if other information is known.
The variables in the kinematic equations are acceleration initial velocity final velocity. 0422 Lecture Notes - Indefinite Integral Introduction and 4 Kinematic UAM Equation Derivationsdocx page 2 of 2 We used a definite integral this time and we have another UAM equation. V U A T This equation is one of the SUVAT equations.
Ive been given the 4 kinematic equations for constant acceleration. And yes there is one more kinematic equation we can solve for. And then expanded to yield.