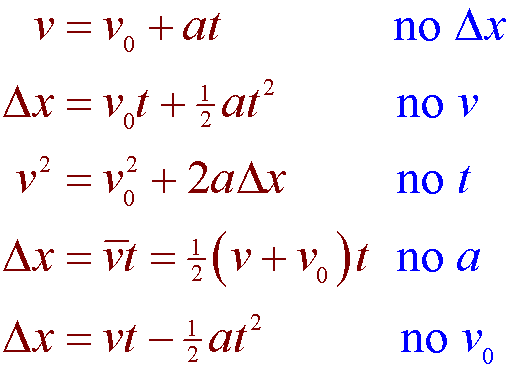Smart Physics Kinematic Formulas

Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another.
Physics kinematic formulas. Uniform acceleration This is the equation of the line of the velocity vs time graph when an object is undergoing uniform acceleration. The branch of physics that defines motion with respect to space and time ignoring the cause of that motion is known as kinematics. This video is part of an online course Intro to Physics.
The Physics Classroom takes a common-sense approach to using the kinematic equations to solve Physics word problems. The slope is the acceleration The intercept is the initial velocity v f at v 0. The variables include acceleration a time t displacement d final velocity vf and initial velocity vi.
Kinematic Equations for Linear Motion For constant acceleration ONLY To select the appropriate equation to solve a particular problem. The kinematic formulas are a set of formulas that relate the five kinematic variables listed below. It does not take the reference of causes of the motion ie forces etc.
This page demonstrates the process with 20 sample problems and accompanying. Derivation of Kinematic Equations View this after Motion on an Incline Lab. Displacement denoted by Δx.
Displacement when object accelerates from rest. Why is the time interval now written as t If we know three of these five kinematic variables for an object under constant acceleration we can use a kinematic formula see below to solve for one of the unknown variables. Calculus is an advanced math topic but it makes deriving two of the three equations of motion much simpler.
Not a truly complete list of formulas though as some things are missingI cant think of any more formulas for this cheat sheet though so suggestions on what to add would be helpful. 1 List what quantities are given - will be 3 2 List what is being asked for - will be 13 Find the equation in the table that contains all 4 involved quantities. Dynamics F ma F force m mass a acceleration Newtons Second Law.