Casual Koh Decomposition Reaction

Please tell about this free chemistry software to your friends.
Koh decomposition reaction. Reactions with inorganic compounds. KOH was found to catalyze the reaction more than NaOH. A decomposition reaction is a type of reaction in which a compound breaks down to form simpler compounds.
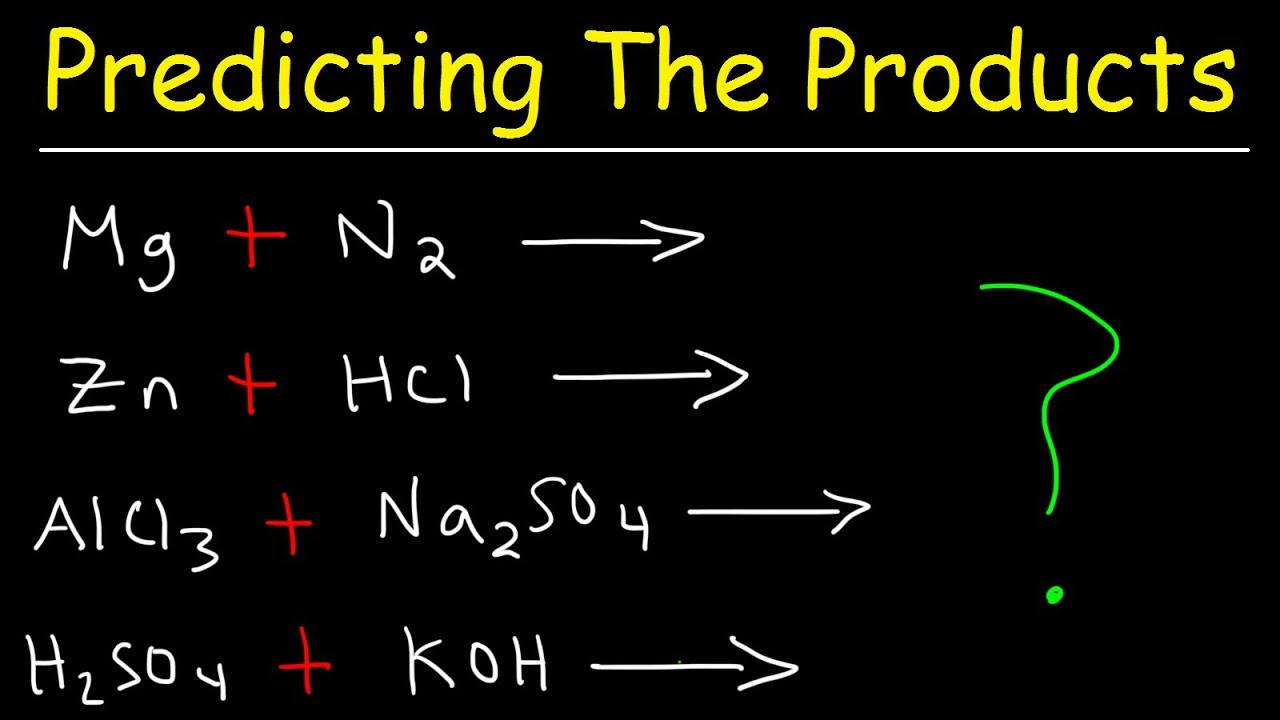
In this video we will describe the equation KOH H2O and write what happens when KOH is dissolved in waterWhen KOH is dissolved in H2O water it will diss. Potassium hydroxide is also a precursor to other potassium compounds. Classify each chemical reaction.
Decomposition reaction is a reaction involving the break down of a single larger chemical species into two or more smaller species. I who observed for similar precoverages of sodium a hydrogen desorption peak near 500 K. ZnB KPO19 ܬܐܘ KOH NHCH Decomposition d SIO 5 Combustion O c.
The above reaction is not a decomposition reaction rather it is a single displacement reaction as K displaces H from water to form KOH liberating H2. There was definitely a reaction. Chemistry questions and answers.
The velocity also increased with increasing alkali concentration but not linearly. Tlus peak was attributed to decomposition of the waterNa reaction product. Complete reactions based on type glem were were needed and balance Single Displacement a.
The abovementioned decomposition path contrasts that of KOH multilayers where also evolu- tion of. Molten KOH is used to displace halides and other leaving groups. This reaction is manifested by the greasy feel that KOH gives when touched fats on the skin are rapidly converted to soap and glycerol.