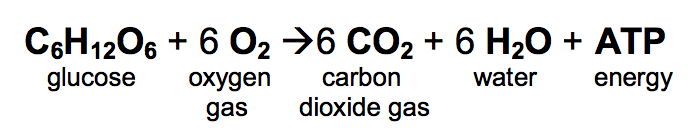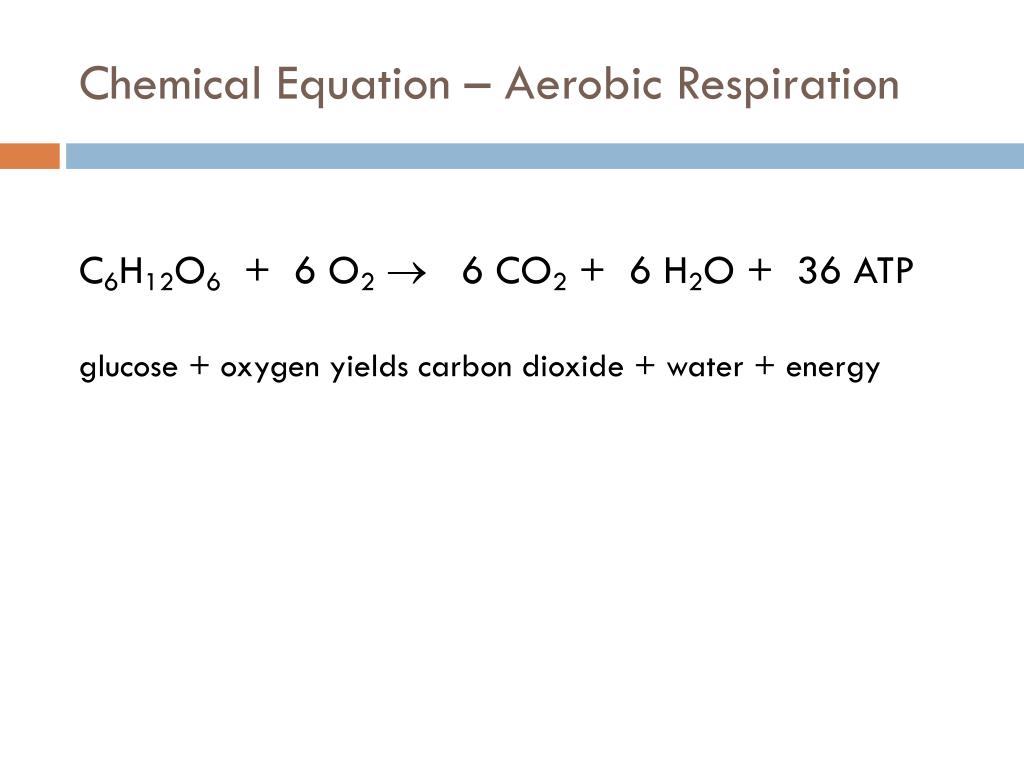Glory Net Equation For Cellular Respiration

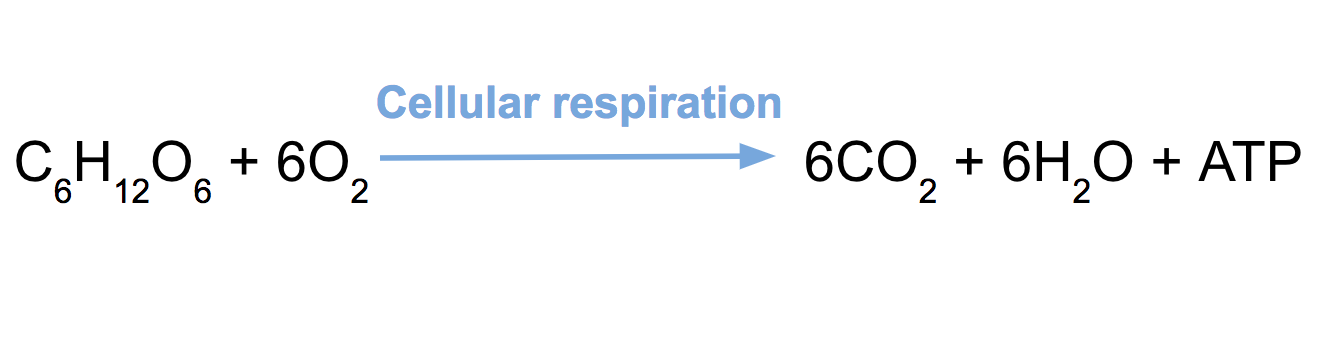
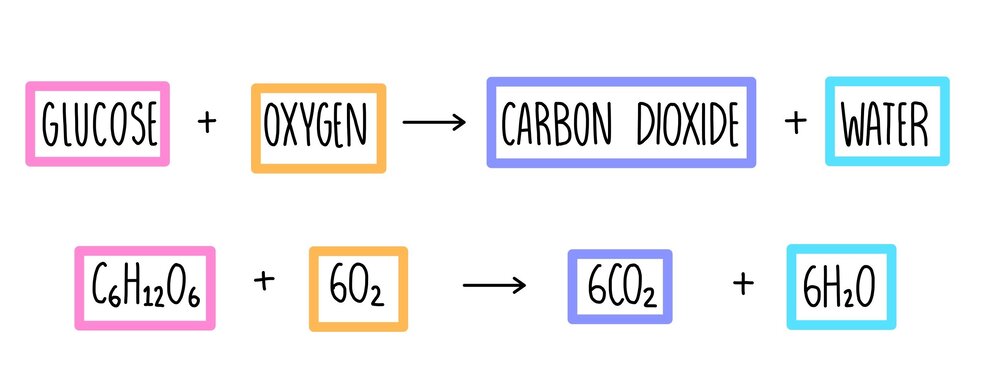
C 6 H 12 O 6 6O 2 6CO 2 6H 2 O glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water 38 ATP.
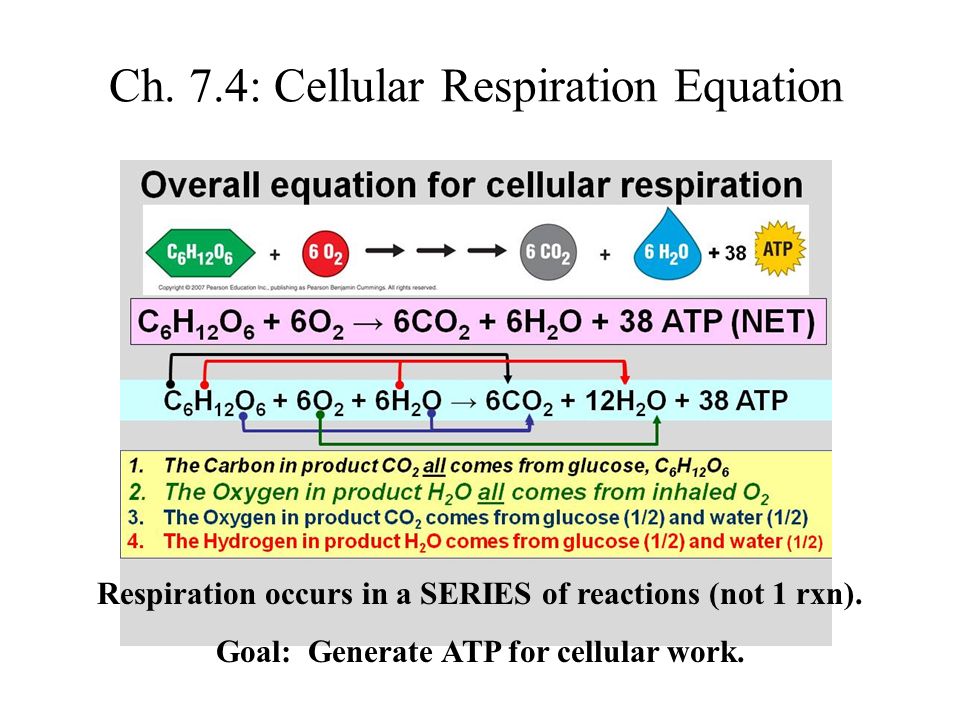
Net equation for cellular respiration. C6H12O6 6O2 6 CO2 6H2O 38 ATP Glycolysis is a ten-step process that occurs in the cytoplasm. Circle the reactants and underline the products. The net equation for cellular respiration is as follows.
Cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions but they can all be summed up with this chemical equation. The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and ADP to produce carbon dioxide water and ATP. Cellular respiration can either be represented using a word or a chemical equation.
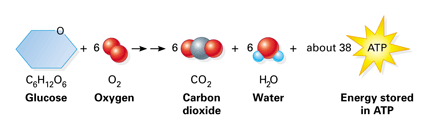
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration. Light dependent Light energy pigments in photosystem I PS II in thylakoid membrane Aerobic respiration ETC provides energy for photolysis of H2O H2O is split into H O2 waste and electrons. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O Energy where the energy that is released is in chemical energy in ATP vs.
Photosynthesis Cellular respiration 2 stages ETC and proton pump Produces and requires ATP Involves compounds. The Cellular Respiration Process The metabolism of glucose to yield energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP and CO2 carbon dioxide a waste product in this equation is known as cellular respiration. In order to balance the equation for cellular respiration a 6 must be added in front of the oxygen carbon dioxide and water.
Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as. This formula could also be read as. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products.
Glycolysis produces a net of 2 ATP molecules C. The Krebs cycle produces a maximum of 2 ATP per molecule of pyruvate D. Glucose and oxygen are the reactants and the end products are carbon dioxide and water with the liberation of energy in form of atp.