Unbelievable Yeast Fermentation Equation
Carbon dioxide is the compound that humans breathe out and plants consume.
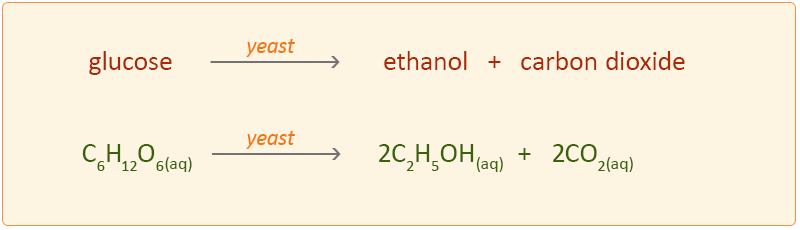
Yeast fermentation equation. The following equation summarizes the chemical changes that occur in cellular respiration of the monosaccharide glucose when oxygen is available. 1 2 Stage 1. The overall chemical equation for the fermentation of a fermentable sugar such as glucose by an enzyme such as zymase is.
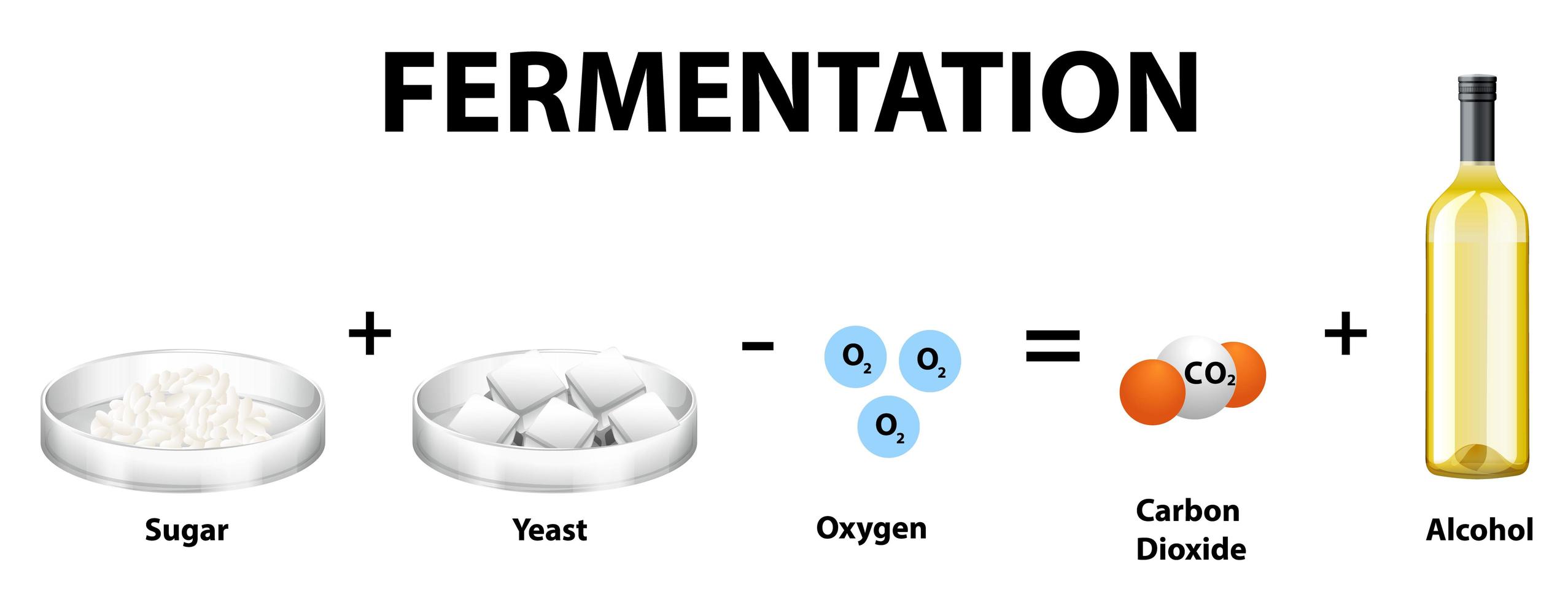
Activation of students prerequisite knowledge. In the fermentation process sugar breaks down in the presence of the yeast enzyme zymase. The balanced equation for fermentation is glucose ethanol carbon dioxide C 6 H 12 O 6aq 2 C 2 H 5 OH aq 2 CO 2 g The carbon dioxide gas bubbles out of the solution.
Alcoholic fermentation converts one mole of glucose into two moles of ethanol and two moles of carbon dioxide producing two moles of ATP in the process. The question that we wanted to answer was Do all sugars undergo yeast fermentation at the same rate Sugar fermentation results in the production of ethanol and carbon dioxide. The reaction conditions for fermentation are.
The basic chemical equation of fermentation is. C6H12O6 6 O2 Æ6 CO2 6 H2O ATP. Yeast fermentation is a digestive process that it used to perform growth and reproduction.
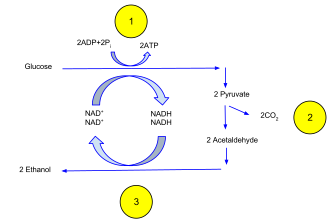
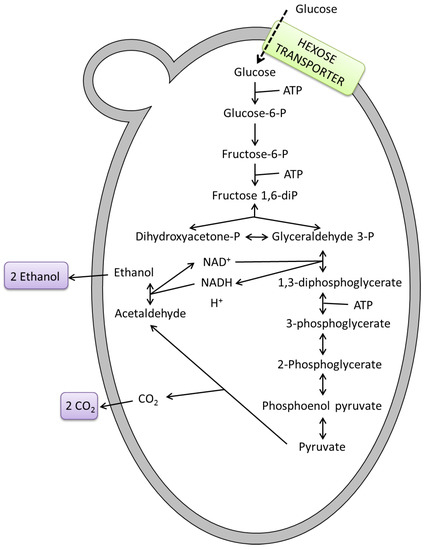
The amount of glucose used for cellular energy can be estimated by a simple mass balance equation and approximate stoichiometric equations relating the amount glucose consumed to the amount of ethanol or biomass produced. This foaming fermenting mixture is called barm and many years ago it was the practice to take the barm from beer fermentations to leaven bread. The main function of fermentation is to convert NADH back into the coenzyme NAD so that it can be used again for glycolysis.
The chemical equations below summarize the fermentation of sucrose into ethanol. In bread carbon dioxide provides the light airy texture of. Cellular respiration is the process that cells use to transfer energy from the organic molecules in food to ATP.