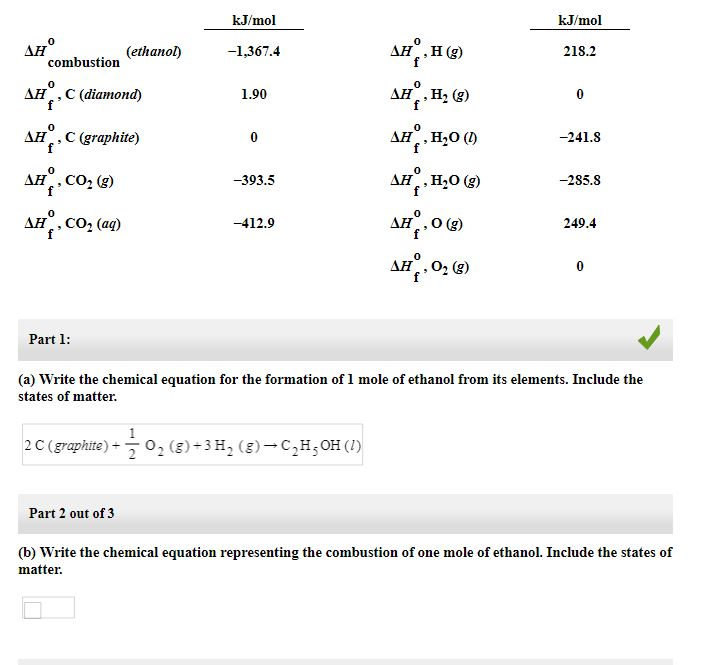
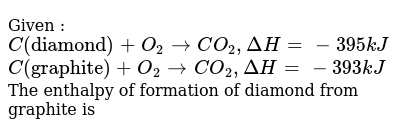Unique Combustion Of Graphite Equation

Standard enthalpy of combustion of ethanol 1368 kJ mol 1 Standard enthalpy of combustion of hydrogen 286 kJ mol 1.
Combustion of graphite equation. 9 this formula would predict a heat of combustion of 0. This problem illustrates the use of Hess Law to compute an enthalpy change that is. Hence the amount of heat liberated can be considered as standard heat of combustion of graphite.
Glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 can be converted into ethanol. Carbon occurs in two forms. State the equation for the formation of ethane C2H6 from its elements and then determine the value for the standard enthalpy of formation of ethane given the following standard enthalpies of combustion.
The values for the enthalpies of combustion of carbon. Ethane C2H6 reacts with oxygen O2 to make carbon dioxide CO2 and water H2O. Complete combustion does NOT give carbon monoxide or sootCheck me out.
The enthalpy of combustion of methane graphite and dihydrogen at 298K are 8903 kJ mol1 3935 kJ mol1 and 2858 kJ mol1 respectively. However above equation also represents combustion of graphite. In thermodynamical terms it is the negative of the enthalpy change for the combustion reaction.
For the formation of each compound write a balanced chemical equation corresponding to the standard enthalpy of formation of each compound. 1 Solution to part a. There are 16 carbon atoms and 32 hydrogen atoms in 1 mol of palmitic acid so the balanced chemical equation is.
C s O 2 g CO 2 g. Reaction of carbon with air Carbon as graphite burns to form gaseous carbon IV oxide carbon dioxide CO 2. 6Cs graphite 3H2g -- C6H6l Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic and what is the enthalpy of reaction.