Fantastic Equation Of Velocity
The most common way to calculate the constant velocity of an object moving in a straight line is with this formula.
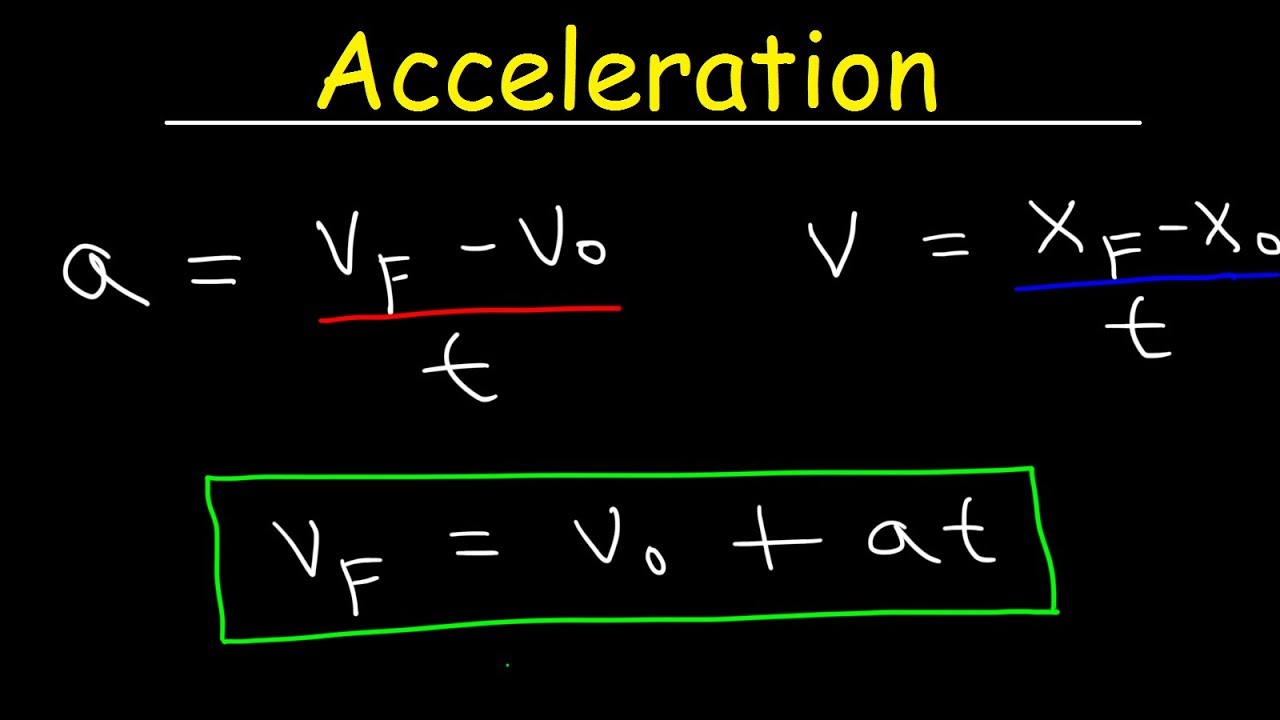
Equation of velocity. These three equations of motion govern the motion of an object in 1D 2D and 3D. Consider an object moving along a straight line with a uniform acceleration a. R d t r is the rate or speed sometimes denoted as v.
When written as a formula the equation is. It is the highest pressure found anywhere in the. In simple words velocity is a measure of how much time an object takes to reach a destination with direction.
V 2πr T Note that 2πr equals the circumference of the circular path. Also its unit is meter per second ms. Equations of motion of kinematics describe the basic concept of the motion of an object such as the position velocity or the acceleration of an object at various times.
The kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be utilized to predict unknown information about an objects motion if other information is known. Velocity acceleration and distance This equation applies to objects in uniform acceleration. Bernoullis equation states that for an incompressible frictionless fluid the following sum is constant.
The equations can be utilized for any motion that can be described as being either a constant velocity motion an acceleration of 0 mss or a constant acceleration motion. P 1 2ρv2 ρgh constant P 1 2 ρ v 2 ρ g h constant. The circular velocity of an object is calculated by dividing the circumference of the circular path by the time period over which the object travels.
Velocity v is a vector quantity that measures displacement or change in position Δs over the change in time Δt represented by the equation v ΔsΔt. 1 to va 333 ms - 0 ms 2 167 ms. The average velocity can be calculated with eq.













